In this article you will find the following:
You finally get around to deleting those unused or problematic apps cluttering your Mac? Or you’re organizing your Mac by moving files to your external drive and encounter a problem that your device won’t let you? Then you know what an “error code 43” message is, and now you’re stuck.
There are several reasons why this message could be popping up:
- The file could be used by another app at the time
- The file name includes prohibited symbols
- The file hasn’t been fully copied or downloaded
- You don’t have permission to access the file
- Finder may be failing to respond.
As you can see, there’s no shortage of reasons why an error 43 message could be popping up, but there is a solution.
Before we begin
Mac’s error code 43 is especially frustrating while deleting some apps. We tend to clog our devices with apps we don’t need or use — a bad habit that can slow down your device. While deleting them manually might seem like the obvious solution, it isn’t the most effective or reliable.
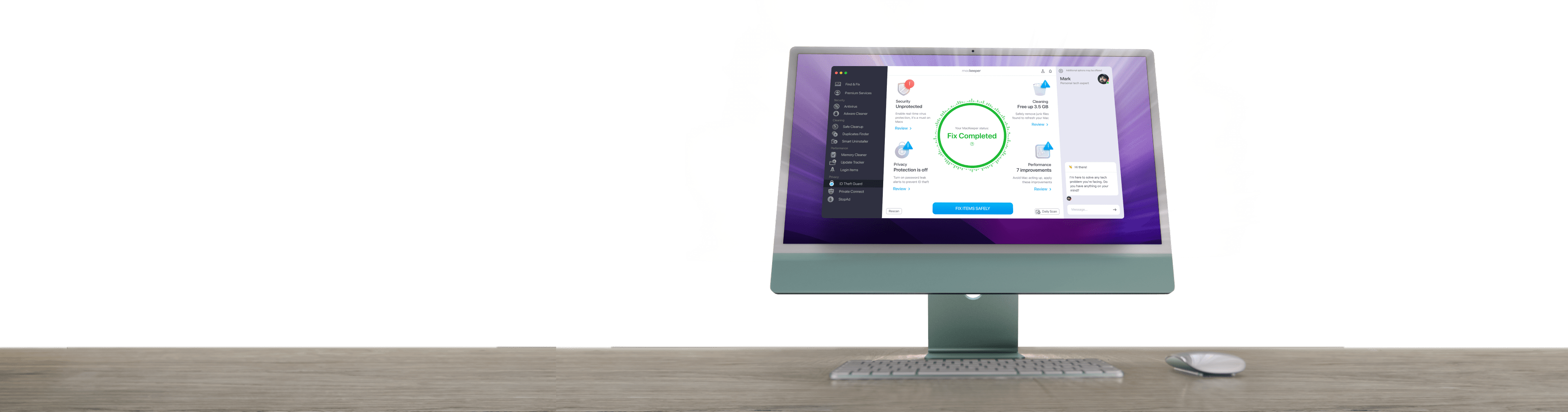
Consider deleting unused apps on your Mac—but if you want to do this thoroughly, use the right software. MacKeeper is an all-in-one cybersecurity app that helps to optimize and protect your Mac. Its Smart Uninstaller helps to find and delete apps and all their related files at the click of a button. See it for yourself.
- Download MacKeeper on your Mac
- Select Smart Uninstaller in the left pane
- MacKeeper will show you all the files it recommends you get rid of, and the amount of memory they’re taking up on your Mac. Click the blue Remove Selected button at the bottom of the screen.
That’s it. Now that you know how to properly and thoroughly remove unwanted apps and files on your Mac, let’s move on to the crux of the matter. Continue reading to learn how to fix code 43 on Mac.
What is error code 43?
First things first: what exactly is an error 43 code, and what does it mean? According to Apple’s community forum, an error 43 code reads as “the operation that can't be completed because one or more required items can't be found.”
It simply means you can’t complete the action you’re taking, like…
- Deleting an app
- Moving media files (like photos) to your external drive, like a USB stick
- Or copying files
… because Mac can’t find the file in question.
This issue could occur as a sign that the file is corrupt, no longer available on your Mac, or the location where it’s stored doesn't include any shared points. There could even be an issue with the folder it’s in.
Error code 43 typically shows up on MacBook devices running OS X El Capitan, although it can also show up on devices running other Mac operating systems. So, whether you’re using a MacBook Pro or another device, this article should prove helpful to you. Let’s get started.
How to get rid of error code 43 on Mac?
Maybe you’ve tried to identify and fix the error 43 issue already, only to find Mac diagnostics not working. Fortunately, you don’t have to abort the mission or throw your Mac against a wall out of frustration. There are a few ways to fix error code 43 on your Macintosh device, so that everything works accordingly again.
The methods to fix the error code include…
- Force quitting Finder
- Resetting PRAM or NVRAM
- Unlocking the file using Terminal
- Fixing the issue using First Aid
- Deleting files in Safe Mode
- Creating a new user.
Let’s look at each solution individually. Follow all the steps carefully.
Force Quit Finder
Sometimes, sorting out the error 43 issue is as simple as force quitting Finder. Finder is, as the name suggests, where you go to find nearly anything on your Mac. It’s where you can locate and manage your drives, downloads, desktop files, applications, recent files, and other documents.
Follow the steps below to force quit Finder:
- Click on the Apple menu in the top-right corner of the screen and select the Force Quit option
- In the pop-up window showing a list of apps, find and click on Finder, then click the Relaunch button
- A pop-up window will appear with a message asking if you’re sure you want to relaunch Finder, click the Relaunch button on the window.
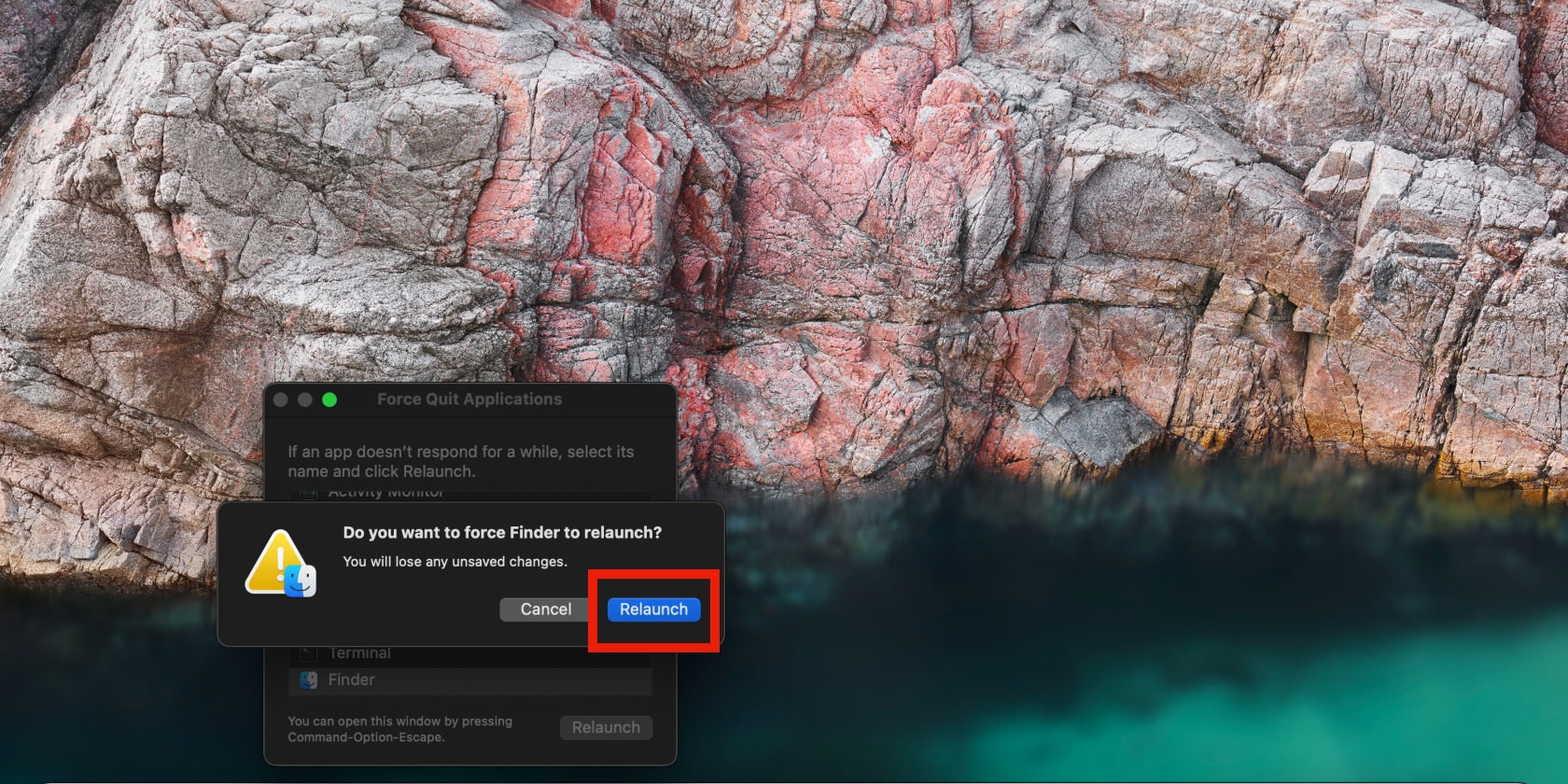
You can also force quit Finder manually using Activity Monitor. Here’s how:
- Press the Command + space bar keys to launch Spotlight search
- Type Activity Monitor in the search bar and select it when it comes up
- Select Finder on the list, click on the x at the top, then click the Force Quit option on the pop-up window that appears. (Another easy way is to access and open Activity Monitor is by going to Finder, selecting Applications, clicking on Utilities, and then finally, clicking on Activity Monitor.)
Encountering an error code 43 is like experiencing a kernel panic on Mac and can be just as frustrating.
A kernel panic happens when your Mac suddenly restarts due to a problem and shows you a message notifying you about the issue. This can happen after you’ve updated to a macOS or other software that is not compatible with your Mac.
Much like an error code 43, a kernel panic can be a huge inconvenience if you’re working on something important, but fortunately, it can be fixed. Learn how to fix kernel panic on Mac in case you come across this issue in the future.
Reset PRAM or NVRAM on Mac
In some cases, your Mac’s Parameter Random Access Memory (PRAM) or Non-Volatile Random Access Memory (NVRAM) might be the issue, so let’s fix it.
Before we move forward, you might be wondering what these big words mean. You’re probably already familiar with the term “Random Access Memory” or RAM.
- PRAM stores the main details of your computer’s operating system. This includes your Mac’s display settings, speaker volume, display resolution, startup disk, and more. PRAM doesn’t reset when your computer switches off.
- NVRAM, on the other hand, does the same thing as PRAM—it’s just the new terminology used by Apple. Simply put, older Macs have PRAM, while Intel-based Macs have NVRAM. Below, we’ll show you how to reset both PRAM and NVRAM on Mac. Follow the guide that applies to you.
Follow the steps below to reset PRAM on Mac:
- Turn your Mac off
- Press and hold the Option/Alt + Command + P + R keys simultaneously until your Mac starts up for the second time. You’ll know it’s starting up when the Apple logo appears and disappears (on newer MacBooks) or when you hear a chime (on older MacBooks).
Follow the guide below to reset NVRAM on Mac:
- Close all apps on your Mac, then go to Finder, click on Applications, select Utilities, and then open Terminal
- Enter the command “sudo nvram -c” in the window and hit the Enter/Return key. You may be prompted to enter the administrator password. Enter it and hit the Enter/Return again
- Now enter the command “sudo shutdown -r now” in the Terminal window and hit Enter/Return. Your Mac should now restart.
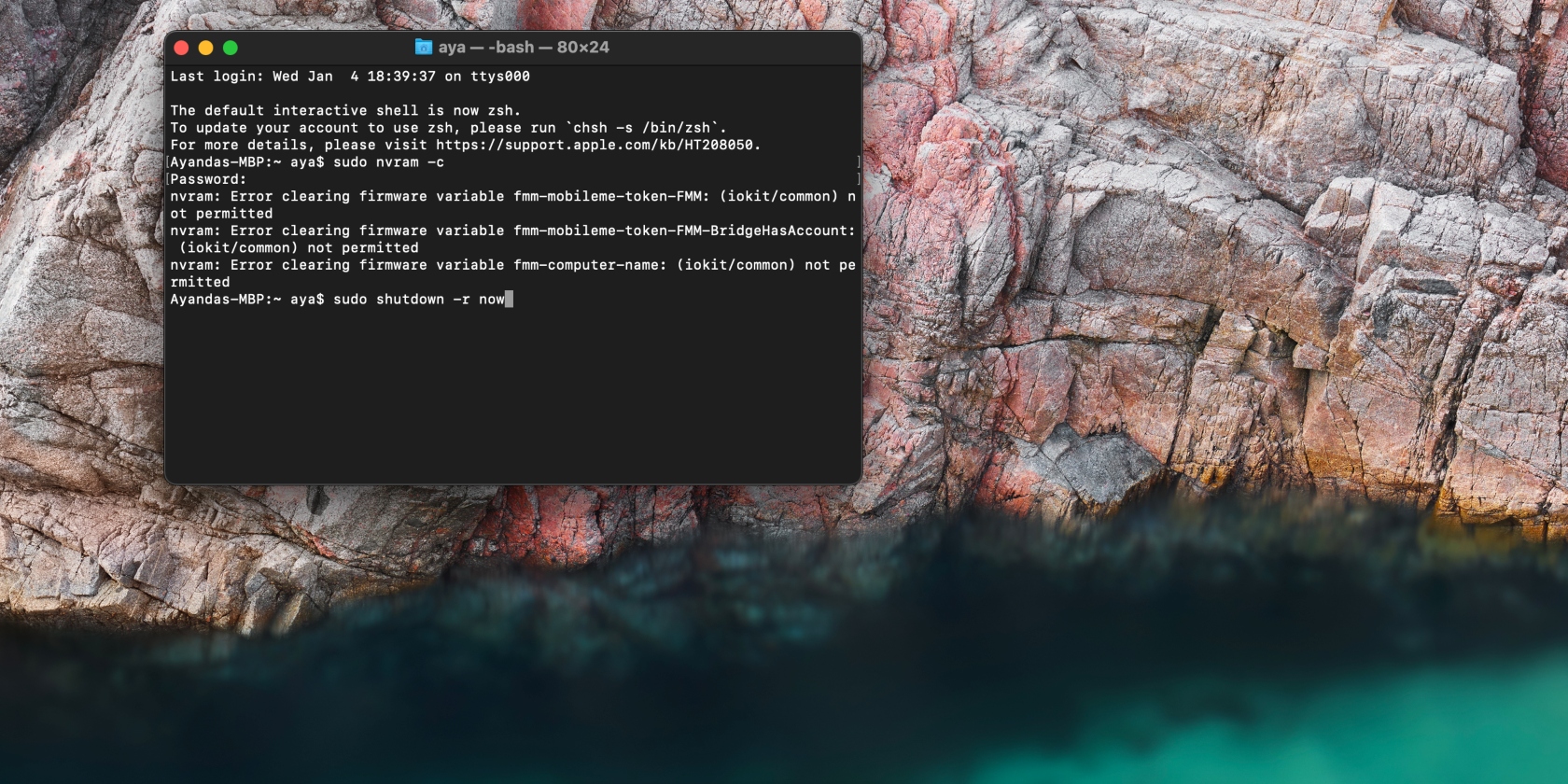
Unlock files with Terminal
You might be getting the error 43 message because the file you’re working with is locked. Below is the method you must follow to unlock it on Mac.
- Open the Terminal app
- Enter the command “chflags nouchg [file path]” but replace the “[file path]” part of the command with the location where your file is stored. To get the file name, select the file, choose Get Info, then copy and paste the information in the Where section into Terminal. For example, “chflags nouchg /Users/aya/Downloads”
- Hit the Enter/return key.
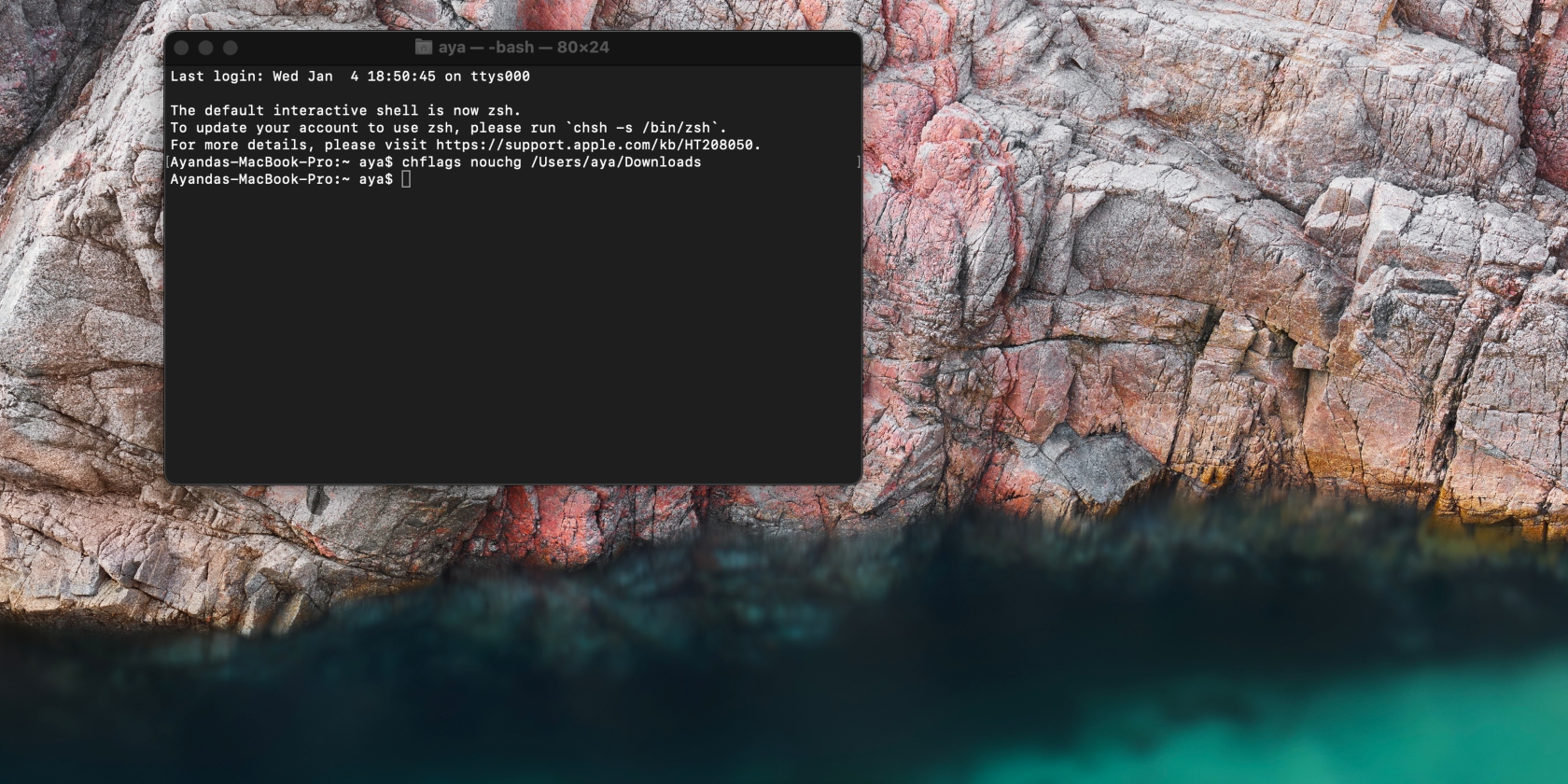
Mac’s Terminal can seem intimidating at first or the first few times you use it, but it’s known to solve a variety of issues on your Mac. You just need to know the relevant command for the specific issue you’re facing, and enter it carefully.
We advise copying it from the source you’re reading and pasting it into the Terminal window. Remember to press Enter/return after entering a command.
A word of caution, though: using Terminal incorrectly can cause even more problems on your Mac. That’s why it’s important to take your cues from a reliable source and follow instructions on how to use certain Terminal commands properly and meticulously.
Not sure where to start? Start by learning how to use Terminal command line on your Mac.
Use Disk Utility First Aid to fix the drive
Disk Utility First Aid is an Apple tool that repairs your device’s disks, including external hard drives, the DDS, SSD, HDD, and more. First Aid can be used to fix error 43 on Mac.
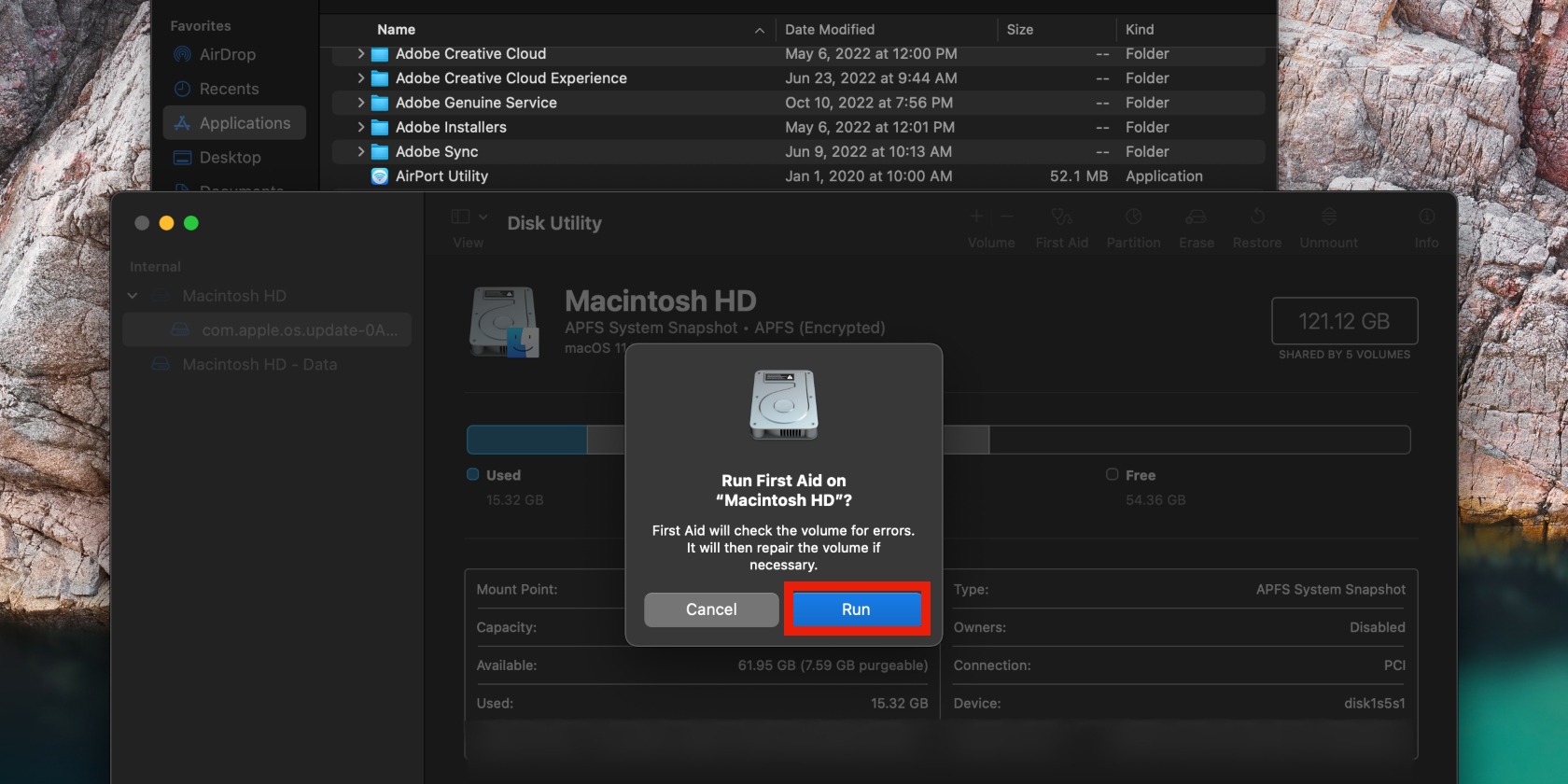
- Go to Finder > Applications > Utilities > Disk Utility
- Select the disk or volume you want to run through First Aid in the left pane
- Now click First Aid at the top of the screen, then click Run and Continue in the pop-up windows that appear.
Delete Files in Safe Mode
Maybe you need a little help deleting the file returning the error message due to system issues? You can force delete it in Safe Mode. Here’s how:
- Go to the Apple menu and select Restart
- Click the Restart option to confirm, and immediately press and hold the Shift key until the login window appears
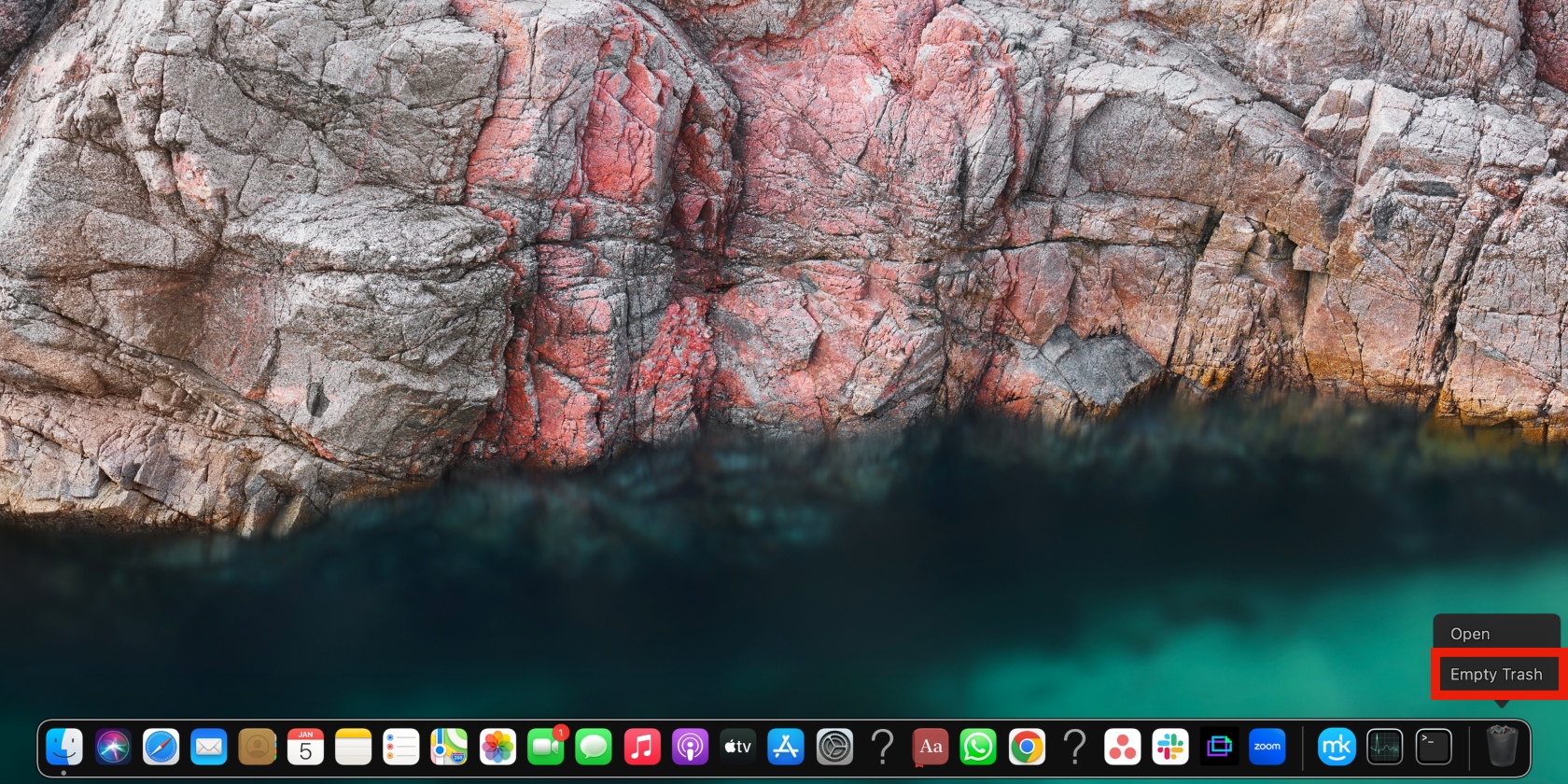
- Now find the file you want to delete, select it and click Move to Trash
- Click and hold the Trash icon and select Empty trash. Select Empty Trash again in the pop-up window to confirm your selection. The item will be deleted permanently.
Create a new user
In some cases, the settings on your user account may be prohibiting you from deleting an item. Consider creating and switching to a new user to delete the item.
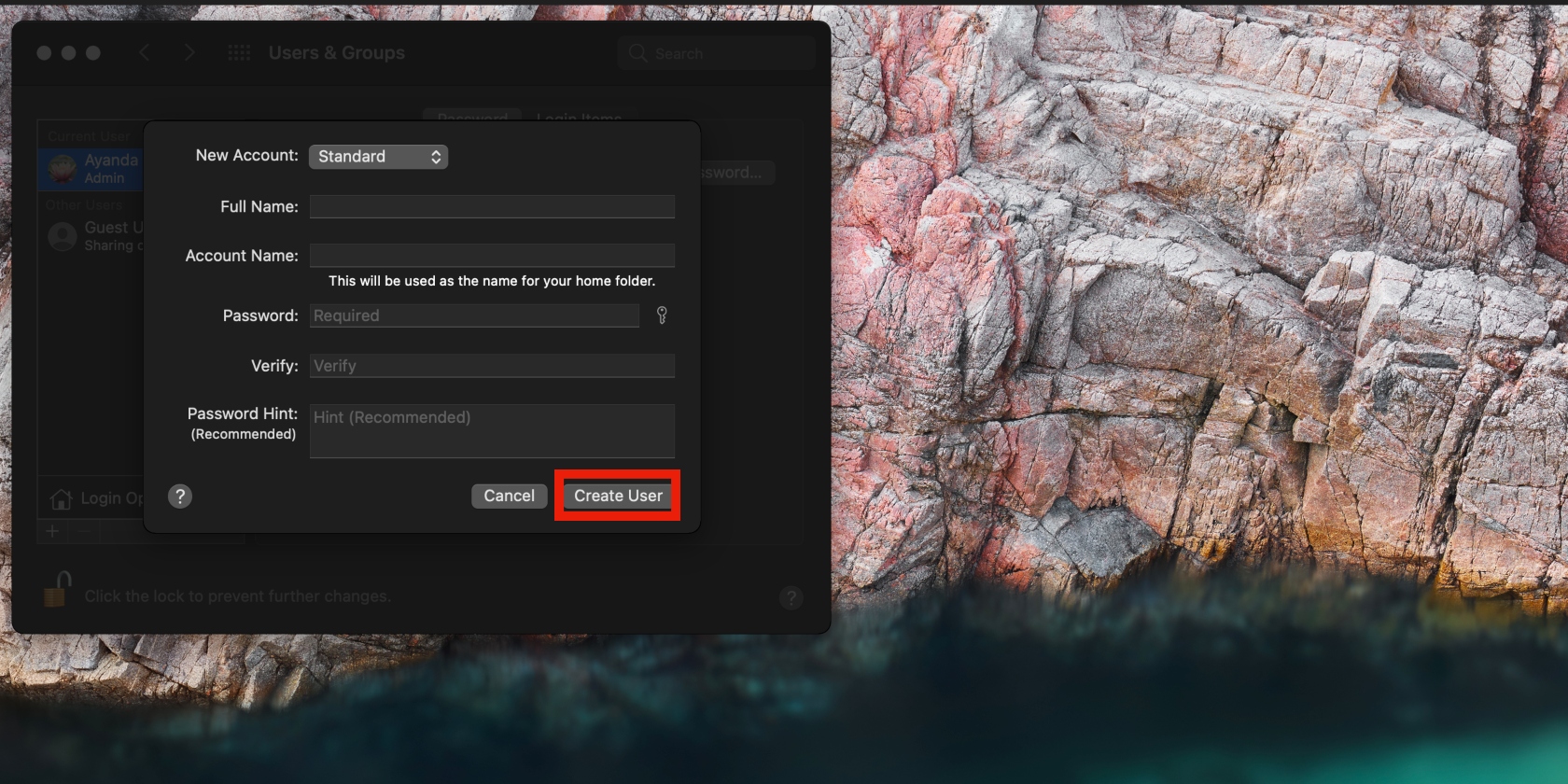
- Go to the Apple menu > System Preferences > Users & Groups
- Click the lock icon and enter your password if prompted to do so
- Now click the plus icon below Login Options and populate the fields in the pop-up window. When you’re done, click the Create User button.
If you don’t need an additional user on your Mac, you can delete the new user once the issue is resolved.
Delete files safely and thoroughly
While Mac tends to run smoothly for the most part, you’ll come across some bumps in the road, like receiving an error 43 message when trying to delete an app or other item.
When this happens, use the tips in this article to successfully delete the item. Most importantly, delete it and other items on your Mac safely and thoroughly using MacKeeper’s Smart Uninstaller. This ensures that no junk files are leftover, optimizes your Mac, and frees up storage.